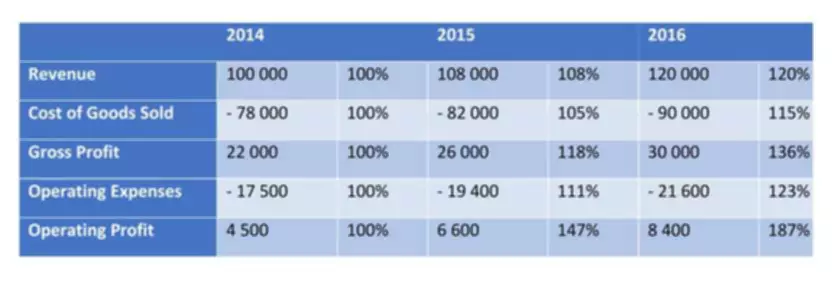
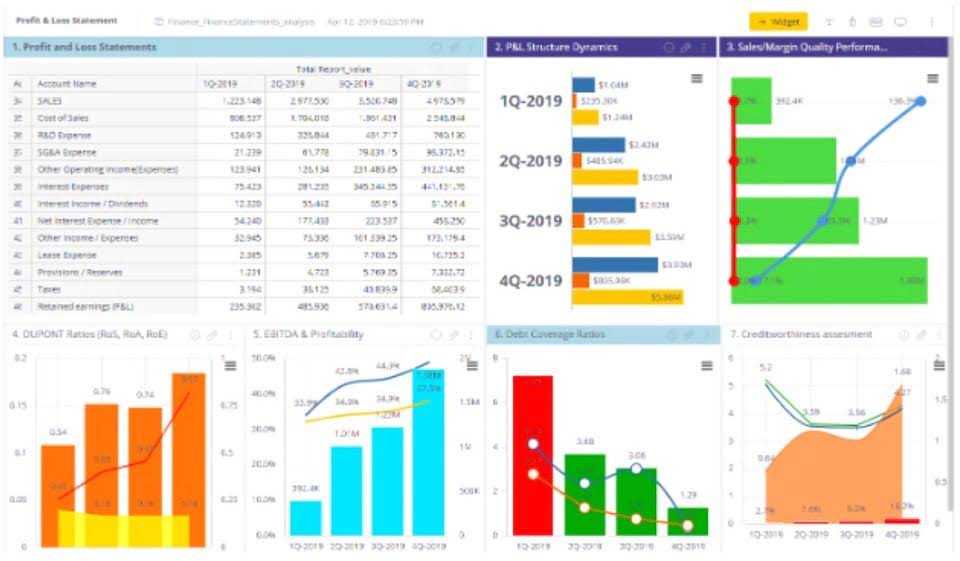
Content
Each department adds direct labor and manufacturing overhead costs, plus the cost of any raw materials it uses. Companies may use separate work-in-process inventory accounts for each department or stage in the process. In accounting, process costing is a method of assigning production costs to units of output. In process costing systems, production costs are not traced to individual units of output. Costs are assigned first to production departments and then to units of output as they move through the departments. The process costing method is typically used for processes that produce large quantities of homogeneous products. The accounting emphasis is in keeping records for the individual departments, which is useful for large batches or runs.
What are the five cost concepts?
Besides the concept of opportunity cost, there are several other concepts of cost namely fixed costs, explicit costs, social costs, implicit costs, social costs, and replacement costs.
Brainyard delivers data-driven insights and expert advice to help businesses discover, interpret and act on emerging opportunities and trends.
Accounting Details
It enables the management to further decision making. Job Costing, as the name implies, allows companies to track the revenues and costs of each job. Job costing systems record revenues and costs for unique units of product that can be easily distinguished from other units of the product. To get the detailed reporting provided by job costing, employees must keep accurate records. Materials and all labor activity including lunches and breaks must be accurately documented and tracked. If not done correctly in project management or accounting software, this can be time-consuming and a source of frustration among employees.
The application of overhead costs during the month . Direct labor costs incurred during the month but not yet paid . The total costs to be accounted for match the total costs accounted for. ATotal costs to be accounted for must equal total costs accounted for https://www.bookstime.com/ . A report that summarizes the production and cost activity within a department for a reporting period. In this article, you will learn what process costing is, the three main types of process costing and how to calculate process costing with an example.
Alternatives to the Process Costing System
In this example, the total cost for the completed products is $280,000 ($28 x 10,000) and the total cost for the incomplete products is $70,000 ($28 x 2,500). The per-unit costs are then split according to the number of units completed & units that are under process. Direct CostDirect cost refers to the cost of operating core business activity—production costs, raw material cost, and wages paid to factory staff. Such costs can be determined by identifying the expenditure on cost objects. Process costing is generally used by manufacturers that produce a large volume of identical items, such as companies involved in oil refining, food production, chemical processing, textiles, glass, cement and paint. Translate the work-in-progress items into equivalent units of finished goods by multiplying the number of unfinished items by their percentage of completion.
The sign is transferred to the finishing department for final materials and labor, before the sign is installed or delivered to the customer. To accurately track these process costs, an information system that allows your staff to easily record this activity is crucial. Hannah also has to keep her staff accountable for using these systems every day because if they don’t, the company can’t track product costs.
How Blockchain Can Be Used In Business
A process costing system accumulates costs and assigns them at the end of an accounting period. At a very simplified level, the process is noted below.
To determine the average cost per unit for the period, the total cost of each process is divided by the total production. There is no last in, first out costing method used in process costing, since the underlying assumption of process costing is that the first unit produced is, in fact, the first unit used, which is the FIFO concept.
Review Problem 4.2
When successive departments are involved, transferred units from one department become all or a part of the direct materials of the next department; however, they are called transferred-in costs, not direct material costs. Direct costs, on the process costing other hand, can easily be traced to specific products or services. If you manufacture face masks, you can calculate the amount of each fabric you use in each mask for direct materials and the direct labor costs it takes to run the machines.
Look at the expense categories and note each overhead cost and the amount spent before. Some of those are fixed costs which can be used to allocate your overhead for this year. Overhead costs are the most difficult to assign to products, and many businesses struggle to analyze these costs. Overhead costs cannot be directly traced to products or services, which makes them harder to track and manage.
The cost of the process is transferred along with the transfer of the product to another process. Homogeneous products with identical and standardized features ensure quality. Many organizations allow each of their departments to operate autonomously. For example, the procurement department will have policies and procedure that are completely unique and independent of those of the supply chain group. This can be an incredibly ineffective way for a business to operate. Harold Averkamp has worked as a university accounting instructor, accountant, and consultant for more than 25 years.
- Profit and loss are calculated after considering the opening and closing balances of finished stock.
- When products have gone through all three stages of production, they are shipped to a warehouse, and the costs are entered into finished goods inventory.
- Direct materials totaling $80,000 are requisitioned and placed into production—$60,000 for the Mixing department, $11,000 for the Testing department, and $9,000 for the Packaging department.
- Prior to the sale of the product, separating production costs and assigning them to the product results in these costs remaining with the inventory.
Processing is typically used when similar units are mass produced. Also process costing system is a type of accounting process costing which is used to determine the cost of a produced inventory.
Toyota Motor Corporation Business Innovation and Philosophy
CThis must match total costs to be accounted for shown in Figure 4.5 “Summary of Costs to Be Accounted for in Desk Products’ Assembly Department”. Although not an issue in this example, rounding the cost per equivalent unit may cause minor differences between the two amounts. Figure 4.5 “Summary of Costs to Be Accounted for in Desk Products’ Assembly Department” shows that costs totaling $386,000 must be assigned to completed units transferred out and units in ending WIP inventory. Manufacturing overhead will be estimated, just as in the job costing method, but will need to be recorded as incurred. The clearing account will be used to accumulate the actual costs, and a reconciliation will be done at the end of each period. Standard cost refers to calculating costs for production units instead of actual costs.
- All expenses—direct and indirect—are accumulated and classified according to the process.
- In this case, we estimate the average level of completion of all work-in-process units, and assign a standard direct labor cost based on that percentage.
- Using a costing system ultimately gives you better information about your company and operations than your competitors.
- During this project, I am going to mention the details of TOYOTA production process system which was developed more than 40 years ago by Taiichi Ohno, the president of Toyota Motor company at that time.
- Once products are delivered to retail stores, product costs are transferred from finished goods inventory to cost of goods sold.
- With the job costing approach, your business completes work on a project basis.